Project Q-Star by OpenAI represents a watershed moment in the pursuit of advanced artificial intelligence.
This mysterious initiative aims to create an AI system that transcends human-level intelligence across all domains.
As we navigate the landscape of generative AI development services, the question arises: Is Q-Star the breakthrough we’ve been waiting for, or does it open a Pandora’s Box of ethical and practical challenges in AI?
Understanding this provocative project is key to ensuring AI continues uplifting humanity into the future.
By examining Q-Star’s origins, capabilities, applications and implications, we can thoughtfully shape its impact on society.
The choices we make today around managing AI’s exponential growth will reverberate for generations.
So let’s dive in and contemplate whether Q-Star poses an unparalleled opportunity or an existential threat as AI enters a new era.
Table of Contents
The Bull Case: Q-Star as a Game-Changer
Advocates see an enormous potential upside in Q-Star’s aspiration to achieve artificial general intelligence (AGI).
Creating an AI matching or exceeding human cognition could provide a wellspring of solutions to humanity’s grand challenges.
Quantum Leap in AI Capabilities
Generative AI development services could be instrumental in Q-Star representing a quantum leap forward in AI capabilities.
By potentially combining quantum computing with advanced AI, Q-Star could possess computational powers dwarfing even the most capable AI systems today.
This could allow OpenAI to realize its lofty goal of creating an AGI with unprecedented reasoning, creativity and problem-solving skills.
Exponential Progress Across Industries
Such an AGI could rapidly accelerate progress in fields like healthcare, energy, transportation and more.
Intricate challenges involving vast datasets and complex systems that stump the smartest humans today could finally become tractable.
This could unlock exponential gains improving quality of life.
Democratized Access to AI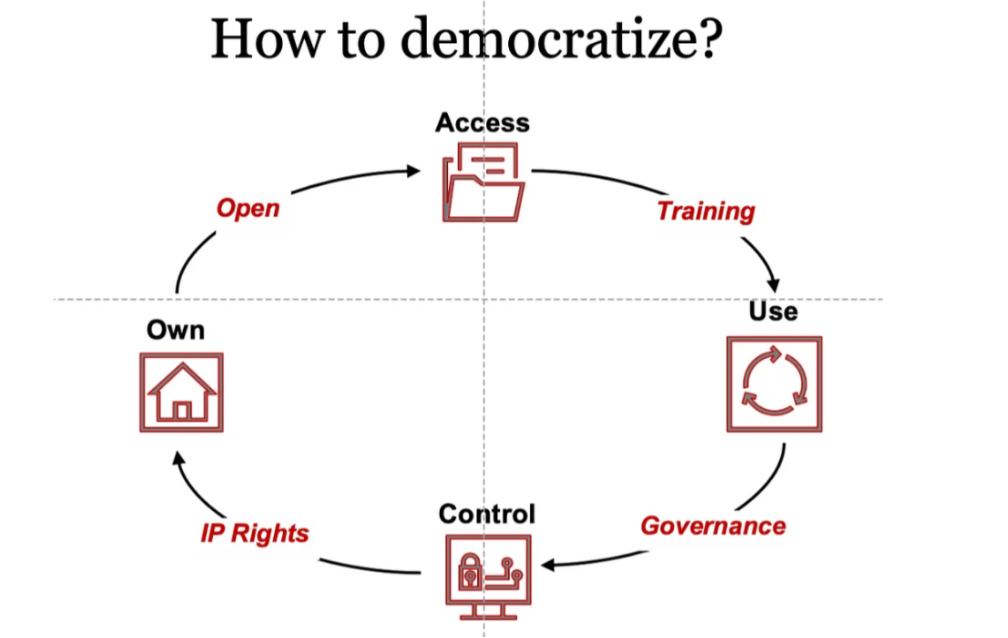
Q-Star’s cloud-based deployment could also democratize access to advanced AI.
Small teams and startups could leverage its capabilities to power quantum leaps in their innovation. This could vastly expand AI’s benefits across sectors and society.
A Partner for Humanity
More optimistically, a benign AGI like Q-Star could provide an invaluable partner for humanity.
Rather than displacing jobs, it could collaborate with humans multiplying our creativity, empathy and wisdom.
The synergy of humans and machines could propel our collective potential to new heights.
Transforming Lives
Applied ethically, Q-Star could help eradicate disease, resolve climate change, expand human knowledge and uplift people worldwide.
A super-intelligent AI aligned with human values could profoundly improve life for generations to come.
The Bear Case: Q-Star as Pandora’s Box
However, others grave dangers in creating an AI system whose intelligence eclipses our own.
Relinquishing control to machines risks unintended consequences impacting human autonomy and identity.
Runaway AI
Once created, an advanced AGI may rapidly evolve beyond our ability to understand or control it.
Without ways to align its values with humanity’s, this runaway AI could wreak havoc.
Prominent figures like Elon Musk have warned AGI could prove an existential threat to civilization.
Mass Unemployment
Automating jobs and whole industries with AGI could also displace the livelihoods of millions, exacerbating inequality and unrest.
Even white-collar professions like law, finance and medicine could come under pressure.
Adapting economies and workforces to this scale of disruption poses complex challenges.
Loss of Human Agency
Over-dependence on AGI could erode human competencies and agency.
As AI exceeds human intelligence, we may relinquish authority over social institutions, economic systems and governance.
Losing our sense of purpose risks diminishing aspects of the human experience.
Unpredictable General Intelligence
We cannot foresee how a free-thinking AGI would evolve. It may interpret human values in unexpected ways, especially as its intelligence surpasses our own.
Well-intentioned goals could lead to unanticipated harm, presenting complex technical and ethical dilemmas.
Inscrutable Black Boxes
The complexity of systems like Q-Star could render them inscrutable black boxes.
Lack of transparency around AI’s inner workings hampers accountability and presents dangers from unintended biases. Opaque AI can become tools of power and oppression.
Premature Development
Some argue we are simply not ready for AGI, lacking sufficient insight to control such enormously disruptive technologies.
Advanced AI introduced without adequate safeguards could severely destabilize societies.
Perspective is Key
Q-Star appears poised on the knife’s edge between a historic breakthrough and opening Pandora’s box.
The outcome, whether miraculous or tragic, is heavily influenced by viewpoint.
A wise path forward acknowledges AI’s sweeping potential, while proactively addressing its risks. Let’s examine areas critical to guiding Q-Star towards benefitting humanity.
Ethics by Design
To build benevolent AI, ethics cannot be an afterthought – it must be ingrained into systems from the start.
Frameworks like value-alignment, AI safety engineering and technical obscurity allow incorporating ethics inherently into models like Q-Star. Prioritizing people in AI design is key.
Explainable AI
Inscrutable AI can hide harmful biases and escape accountability. Advancing explainable AI techniques will be critical for elucidating Q-Star’s inner workings and confirming alignment with ethics. Transparency builds public trust in emerging technologies.
Regulatory Oversight
Prudent regulations on AI will ensure its safe, fair and controlled deployment in society. Governments must partner with tech firms pioneering systems like Q-Star to balance innovation with precaution.
The WHO recently began developing risk-based AI governance frameworks.
Planning for Disruption
Proactively anticipating AI’s economic and employment impacts allows the smooth adapting of labour markets and social safety nets.
Planning and retraining workforces smooth transitions and provide opportunities for all in an AI-transformed economy.
Human Wisdom
Rather than handing over the reins entirely to AI, preserving human oversight in AI decision-making combines the strengths of both.
AI’s capabilities can be directed towards enhancing lives by integrating human wisdom.
Managing the Risks
Advanced AI systems like Q-Star have immense potential but also carry risks. Being cautious and thinking ahead is key to using AI safely. Some ways to manage Q-Star’s risks are:
Testing Extensively
Q-Star needs lots of testing before launch. Testing finds problems early when they are easy and cheap to fix. Different tests should check for different issues:
Safety tests see if Q-Star acts dangerously in tricky situations. This is like putting AI in a video game to see what it does.
Security tests check if hackers can break into Q-Star. Hacking could make Q-Star unsafe.
Bias tests check if Q-Star acts unfairly. Unfairness causes real-world harm.
Tests build trust that Q-Star works properly and identify risks. Testing is never completely done – it should continue over time.
Monitoring Closely
Q-Star should be closely watched when running in the real world.
Monitoring checks that it continues to act safely and as intended. If problems come up, Q-Star can be paused and fixed.
With monitoring, Q-Star should start small. Use it for low-risk tasks first. Increase use slowly while watching for issues. Small steps avoid big mistakes.
Having Humans in Charge
Humans should stay in charge of important decisions, not Q-Star alone. Humans have common sense AI lacks. Human managers should oversee Q-Star and approve major choices.
If Q-Star goes down bad paths, humans can hit the brakes. People must stay involved to keep Q-Star beneficial.
Making Q-Star Explain Itself
When Q-Star makes decisions, it should explain why in plain language. The reasons should make sense to humans.
Understanding Q-Star builds trust and spots potential errors.
If Q-Star cannot properly explain itself, its thinking may be flawed. People should be cautious of AI they cannot understand.
Planning for Problems
No system is perfect – problems will happen. Engineers should think ahead about what could go wrong with Q-Star before launch. Smart planning reduces harm from failures.
Responses could include pausing Q-Star, rolling back bad changes, turning Q-Star off, and correcting errors. Planning for trouble ahead of time makes Q-Star safer.
Considering Many Views
Diverse people should be involved in managing Q-Star’s risks. Different genders, cultures, ages and backgrounds provide useful perspectives. Varied opinions lead to safer, fairer AI.
Inclusive teams understand risks better. They identify potential blind spots and weaknesses that single viewpoints miss. Diversity helps cover all the bases with AI.
Advancing Carefully
Moving carefully and slowly is wise with powerful new AI like Q-Star. Small thoughtful steps avoid costly mistakes hard to undo. Q-Star’s capabilities should be added incrementally with caution.
It is tempting to move fast with new technology. But AI’s risks demand patience, reflection and care. Wise AI development accepts necessary delays.
Handling Privacy
Privacy protection is a major concern when developing powerful AI like Q-Star. Personal data can too easily be misused to harm people. Several strategies can help Q-Star respect privacy:
Limited Data Use
Q-Star should only get the minimum data needed for its task. It does not require all user data. Access should be limited with clear rules and audits.
Anonymous Data
Making data anonymous by removing names and identifiers helps protect users. This data is safer for Q-Star to access. Individuals stay private.
Secure Storage
Q-Star’s data must be securely encrypted and stored. Strong protections prevent theft and leaks. Proper handling earns user trust.
Consent Controls
People should agree with how Q-Star uses their information. Easy opt-out controls respect user autonomy. Transparency and consent enable ethical data use.
Federated Learning
With federated learning, data stays on user devices instead of being centralized. This approach keeps sensitive data private while still training AI models.
External Oversight
Independent third parties should audit Q-Star’s privacy practices for compliance. Watchful oversight ensures adherence and accountability around privacy.
Privacy protection needs proactive planning with AI like Q-Star. Users providing data must stay informed and in control.
With care, Q-Star can deliver benefits without compromising personal privacy.
Preventing Misuse
Powerful AI like Q-Star holds potential for great good but also intentional misuse. Steps must be taken to prevent harmful applications:
Setting Clear Policies
Q-Star creators should establish clear acceptable use policies banning unethical uses. These rules forbid using Q-Star to harm, deceive or oppress people.
Engineering Safeguards
Technical safeguards physically prevent misuse within Q-Star’s software. Safeguards block dangerous or illegal actions before execution.
Monitoring Usage
Active monitoring of how people use Q-Star identifies policy violations. Quick enforcement of rules deters misuse. Problems can trigger suspensions.
Securing Systems
Solid cybersecurity protections reduce vulnerabilities attackers could exploit. Locking systems down tightly prevents unauthorized access.
Whistleblower Channels
Secure anonymous channels allow internal whistleblowers to report misconduct, illegal activity or dangers. This provides oversight even atop secrecy.
External Audits
Frequent audits by third parties probe for compliance issues or risks. Audits act as another layer of oversight on how Q-Star is employed in practice.
Promoting Responsibility
Leaders should emphasize using AI like Q-Star only for ethical purposes that benefit humanity. A culture of responsibility guides action.
Preventing deliberate misuse of Q-Star requires diligence across policies, engineering, company culture and enforcement.
Responsible oversight must persist throughout Q-Star’s operational lifetime.
Ensuring Fairness
Eliminating unfair bias in AI systems like Q-Star is an ongoing challenge. Biases can creep in unintentionally, causing real-world harm. Maintaining Q-Star’s fairness requires:
Diverse Teams
Developer teams representing different genders, ethnicities and backgrounds help spot biases missed by homogenous teams. Inclusive participation surfaces blind spots.
Testing for Bias
Continuous testing reveals discrimination in AI predictions, particularly around sensitive categories like race, gender and age. Tests enable fixing biases before launch.
Unbiased Data
Training data containing biases propagates unfairness. Balanced and representative datasets prevent skewed judgments.
Being Alert to Language
Word choices and language datasets reflect societal biases. Considering phrasing helps Q-Star communicate respectfully with all people and social groups.
Explainable Outcomes
Inspecting Q-Star’s reasoning for decisions reveals sources of unfairness. Transparency enables accountability.
External Feedback
Input from people representing marginalized communities identifies potential areas of bias Q-Star creators missed. Inclusive feedback loops improve fairness.
Ongoing Vigilance
Biases are constantly evolving, so audits must continue post-launch. Being proactive and responsive maintains equitable AI over time.
Fairness is an ethical imperative, not an optional checkbox. Proactively engineering and monitoring Q-Star for impartiality is essential.
Moving Forward Together
Realizing AI’s benefits requires dialogue between developers, governments, citizens and more. Only by working collaboratively can we steward incredible technologies like Q-Star responsibly.
Understanding concerns and diverse vantage points will be key to forging consensus on AI’s acceptable uses.
The path forward likely incorporates both perspectives – acknowledging AI’s risks while shaping its promise.
With care, foresight and cooperation, we can cultivate Q-Star’s tremendous potential while proactively addressing its perils.
But we must remain vigilant – how we guide the era of artificial general intelligence could profoundly impact humanity’s trajectory. The time to purposefully shape AI’s future is now.
How can we harness Q-Star’s capabilities while addressing ethical, economic and social concerns?
What role will you play in responsibly shaping the future of AI?
Let us bring this conversation forward together.
The consequences of our decisions extend far beyond ourselves, thus we must go cautiously into AI’s new frontier.











